从word2vec到negative sampling
到目前为止,word2vec算法不单单是nlp的基础,也成为推荐和搜索的基础,本文记录一下word2vec算法中的negative sampling方案,并基于此记录了其他的sampling方法。
参考链接:
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/76568362/
- https://blog.csdn.net/yimingsilence/article/details/105920987
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/129824834
- https://narcissuscyn.github.io/2018/07/03/CandidateSampling/
- https://www.zhihu.com/question/50043438
- https://blog.csdn.net/wangpeng138375/article/details/75151064
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/45368976
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/45014864
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/27234078
- https://www.cnblogs.com/pinard/p/7249903.html
- https://www.cnblogs.com/peghoty/p/3857839.html
- https://www.zhihu.com/question/386144477
- https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40901056/article/details/88568344
- https://blog.csdn.net/u010223750/article/details/69948463
Skip-gram方法的word2vec
在word2vec出现之前,已经有用神经网络DNN来用训练词向量进而处理词与词之间的关系了。采用的方法一般是一个三层的神经网络结构(当然也可以多层),分为输入层,隐藏层和输出层(softmax层)。
这个模型是如何定义数据的输入和输出呢?一般分为CBOW(Continuous Bag-of-Words 与Skip-Gram两种模型。
CBOW模型的训练输入是某一个特征词的上下文相关的词对应的词向量,而输出就是这特定的一个词的词向量。
Skip-Gram模型和CBOW的思路是反着来的,即输入是特定的一个词的词向量,而输出是特定词对应的上下文词向量。
PS:skip-gram 出来的准确率比cbow 高,cbow比sg训练快,sg比cbow更好地处理生僻字(出现频率低的字)。
在词向量训练任务中,softmax函数有如下:
$$p(w|c) = \frac{\exp(h^\top v_w)}{\sum_{w_i \in V} \exp(h^\top v_{w_i})}=\frac{\exp(h^\top v_w)}{Z(h)}$$
其中,$h$是隐藏层的输出, $v_{w_i}$是w对应的输出词向量(即softmax的权重矩阵),$V$是词典,$c$是上下文。
在神经网络语言模型中,一般会把$C$压缩为$h$。 从上面的公式可以看出,softmax函数的分母是对所有词典进行遍历求和,当$V$的size比较小的时候,softmax的求导以及梯度下降速度较快,但是当$V$的size比较大的时候,softmax的分母需要遍历所有的样本进行求和,因此速度较慢,对于此问题,业界提出了多种方法来解决该问题,常见的方法有Noise Contrastive Estimation(NCE),negative sampling,sampling softmx算法等,接下来分别讲解一下两种算法。
Noise Contrastive Estimation算法
对于每一个训练样本(x, T),我们训练binary classification,而不是multiclass classification。具体一点,我们对于每个样本,拆分成一个真实的(x,y) pair,另外我们随机产生k个Noise的(x,y)pair,这样我们就可以用来训练处这样的binary classifier。
用概率来表示,这个问题由之前的P(y|x) 通过x预测所有y,换成了P(x,y),计算x,y同时存在的概率,换言之,从基于特征x求y的最大后验概率,变成基于特征X和y,共同出现的最大后验概率。
假设共有m个样$(l_i,c_i)$, 建模: \begin{equation} P\left(l_{i} \mid c_{i}\right)=\frac{u_{\theta}\left(l_{i}, c_{i}\right)}{\sum_{i}^{n} u_{\theta}\left(l_{j}, c_{i}\right)}=\frac{u_{\theta}\left(l_{i}, c_{i}\right)}{Z_{i}} \end{equation} 假设负例label从某个分布$Q(l_i)$中抽取, 且抽取$k$次. 正例从上面的分布抽取, 则有: $(l_i,c_i)$真实样本的概率: \begin{equation} P\left(\text { True } \mid l_{i}, c_{i}\right)=\frac{P\left(l_{i} \mid c_{i}\right)}{k Q\left(l_{i}\right)+P\left(l_{i} \mid c_{i}\right)}=P\left(T \mid l_{i}, c_{i}\right) \end{equation} $(l_i,c_i)$负样本的概率: \begin{equation} P\left(\text { False } \mid l_{i}, c_{i}\right)=\frac{k Q\left(c_{i}\right)}{k Q\left(l_{i}\right)+P\left(l_{i} \mid c_{i}\right)}=P\left(F \mid l_{i}, c_{i}\right) \end{equation} 最终最大化log似然估计, 损失函数: \begin{equation} J(\theta) = \prod_{(w,c) \in T} P(T|w,c;\theta) \prod_{(w,c) \in Neg} P(F|w,c;\theta) \end{equation} \begin{equation} L=\sum_{i}^{n}\left(\log P\left(T \mid l_{i}, c_{i}\right)+k \sum_{i=0, L_{x} \sim Q\left(l_{i}\right)}^{k} \log P\left(F \mid L_{x}, c_{i}\right)\right) \end{equation}
negative sampling算法
负采样Negative Sampling是NCE的一个变种,概率的定义有所区别。
建模, 作为二分类softmax损失. \begin{equation} P\left(T \mid l_{i}, c_{i}\right)=\frac{u_{\theta}\left(l_{i}, c_{i}\right)}{1+u_{\theta}\left(l_{i}, c_{i}\right)}=\sigma\left(u_{\theta}\left(l_{i}, c_{i}\right)\right) \end{equation} \begin{equation} P\left(F \mid l_{i}, c_{i}\right)=1-P\left(T \mid l_{i}, c_{i}\right)=\frac{1}{1+u_{\theta}\left(l_{i}, c_{i}\right)}=1-\sigma\left(u_{\theta}\left(l_{i}, c_{i}\right)\right) \end{equation}
最终最大化log似然估计略(和NCE相同), 负例的采样时, 为全体样本的所有$l$不消重的均匀采样,或者每个$l$采到的概率为: \begin{equation} P\left(l_{x}\right)=\frac{\operatorname{cnt}\left(l_{x}\right)^{0.75}}{\sum_{y \in L} \operatorname{cnt}\left(l_{y}\right)^{0.75}} \end{equation}
注意,构造样本时,要注意正负样本的比例,如果考虑所有的负样本,会导致正负比例失衡,模型权重会被负样本带偏。
sampling softmax算法(sampled_softmax_loss)
Sampled softmax方法不同于nce方法,nce是把多分类问题转化成二分类,而sampled softmax方法则是只抽取一部分样本计算softmax。训练的时候不需要特别精准的softmax归一化概率,只需要一个粗略值做back propoagation就好了。这么粗糙的算法,可能会导致分布不一致问题???
如果损失函数采用交叉熵损失函数: \begin{equation} H(q,p) = - \sum_x q(x) \log p(x) \end{equation}
这里q是真实期望分布,例如 $q=[0,…1,…,0]$,p是模型输出分布,对应最上面的softmax公式。
对于一个样本,可得交叉熵损失函数(这里把模型的参数统称为$\theta$): \begin{equation} J_\theta = - \text{log} \dfrac{\text{exp}({h^\top v_{w}})}{\sum_{w_i \in V} \text{exp}({h^\top v_{w_i}})} \end{equation} 假设:$\mathcal{E}(w)=-h^\top v_{w}$, 则: \begin{equation} J_\theta = \mathcal{E}(w) + \text{log} \sum_{w_i \in V} \text{exp}( - \mathcal{E}(w_i)) \end{equation} 对$\theta$求梯度得: \begin{equation} \nabla_\theta J_\theta = \nabla_\theta \mathcal{E}(w) + \sum_{w_i \in V} \dfrac{\text{exp}(- \mathcal{E}(w_i))}{\sum_{w_i \in V} \text{exp}(- \mathcal{E}(w_i))} \nabla_\theta (- \mathcal{E}(w_i)) \end{equation} 已知:$p(w_i) = \dfrac{\text{exp}(- \mathcal{E}(w_i))}{\sum_{w_i \in V} \text{exp}- \mathcal{E}(w_i))}$, \begin{equation} \nabla_\theta J_\theta = \nabla_\theta \mathcal{E}(w) - \sum_{w_i \in V} P(w_i) \nabla_\theta (\mathcal{E}(w_i)) \end{equation}
对于梯度公式的第二部分,可以认为是$\nabla_\theta (\mathcal{E}(w_i))$对于softmax输出$P(w_i)$的期望,即: \begin{equation} \sum_{w_i \in V} P(w_i) \nabla_\theta \mathcal{E}(w_i) = \mathbb{E}{w_i \sim P}[\nabla\theta \mathcal{E}(w_i)] \end{equation} 上面的这个公式就是控制softmax采样需要优化的部分。
根据传统的重要性采样方法,按照如下公式计算期望: \begin{equation} \frac{1}{N} \sum_{w_i \sim Q(w)}\frac{P(w_i)}{Q(w_i)}\nabla_\theta \mathcal{E}(w_i) \approx \mathbb{E}{w_i \sim P}[\nabla\theta \mathcal{E}(w_i)] \end{equation} 其中$N$是从分布$Q$(我们自己定义的一个容易采样的分布)中采样的样本数,但是这种方法仍然需要计算$P(wi)$,而$P(wi)$的计算又需要softmax做归一化,这是我们不想看到的,所以要使用一种有偏估计的方法。
Softmax公式的分母部分: \begin{equation} Z(h)=\sum_{w_i \in V} \text{exp}(- \mathcal{E}(w_i))=M\sum_{w_i \in V} (\frac{1}{M})\cdot \text{exp}(- \mathcal{E}(w_i)) \end{equation} 公式中$\sum_{w_i \in V} (\frac{1}{M})\cdot \text{exp}(- \mathcal{E}(w_i))$是一种期望形式,因而可以通过采样方法进行估计得到$Z(h)$, 对于$Z(h)$的采样候选分布仍旧选择$Q$分布。 则可以得到: \begin{equation} Z(h)=\hat{Z}(h)=\frac{M}{N}\sum_{w_i \sim Q(w)}\frac{\hat{R}(w_i)\text{exp}(- \mathcal{E}(w_i))}{Q(w_i)}=\frac{M}{N}\sum_{w_i \sim Q(w)}\frac{\text{exp}(- \mathcal{E}(w_i))}{M\cdot Q(w_i)} \end{equation} 上式中的$\hat{R}(w_i)$代表概率$\frac{1}{M}$,约去$M$可得: \begin{equation} \hat{Z}(h)=\frac{1}{N}\sum_{w_i \sim Q(w)}\frac{\text{exp}(- \mathcal{E}(w_i))}{ Q(w_i)} \end{equation} 到这里,我们就可以用$\hat{Z}(h)$去近似$Z(h)$了。
现在理一下思路:给定候选分布Q,传统采样方法需要计算P,也就是说需要计算分母Z,这是我们不想看到的。幸运的是分母Z仍然可以通过采样得到,采样Z的时候,仍然采用候选分布Q。
\begin{equation} \frac{1}{N} \sum_{w_i \sim Q(w)}\frac{P(w_i)}{Q(w_i)} \nabla \theta \mathcal{E}(w_i) \approx \mathbb{E}{w_i \sim P}[\nabla _\theta \mathcal{E}(w_i)] \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \frac{1}{N}\sum_{w_i \sim Q(w)}\frac{\hat{P}(w_i)}{Q(w_i)}\nabla \theta \mathcal{E}(w_i) \approx \mathbb{E}{w_i \sim P}[\nabla \theta \mathcal{E}(w_i)] \end{equation} 其中 $\hat{P}(wi)$代表采样方式获得的概率: \begin{equation} \hat{P}(w_i)=\frac{\text{exp}(- \mathcal{E}(w_i))}{\hat{Z}(h)} \end{equation} 可得: \begin{equation} \mathbb{E}{w_i \sim P}[\nabla_\theta \mathcal{E}(w_i)]\approx \frac{1}{N}\sum_{w_i \sim Q(w)}\frac{\text{exp}(- \mathcal{E}(w_i))}{Q(w_i)\hat{Z}(h)}\nabla_\theta \mathcal{E}(w_i) \end{equation} 现在我们就从$Q$分布中采样$N$个样本,组成集合$J$,最终得到: \begin{equation} \mathbb{E}{w_i \sim P}[\nabla\theta \mathcal{E}(w_i)]\approx \frac{\sum_{w_j \in J}\text{exp}(- \mathcal{E}(w_j))\nabla_\theta \mathcal{E}(w_j)/Q(w_j)}{\sum_{w_j \in J}\text{exp}(- \mathcal{E}(w_j))/Q(w_j)} \end{equation} 整体梯度为: \begin{equation} \nabla_\theta J_\theta = : \nabla_\theta \mathcal{E}(w) - \frac{\sum_{w_j \in J}\text{exp}(- \mathcal{E}(w_j))\nabla_\theta \mathcal{E}(w_j)/Q(w_j)}{\sum_{w_j \in J}\text{exp}(- \mathcal{E}(w_j))/Q(w_j)} \end{equation}
Tensorflow的采样方法:candidate sampling
假如我们有一个多分类任务或者多标签分类任务,给定训练集$(x_i,T_i)$,其中xixi表示上下文,$T_i$表示目标类别(可能有多个).可以用word2vec中的negtive sampling方法来举例,使用cbow方法,也就是使用上下文$x_i$来预测中心词(单个target$T_i$),或者使用skip-gram方法,也就是使用中心词$x_i$来预测上下文(多个target($T_i$)).
我们想学习到一个通用函数$F(x,y)$来表征上下文$x$和目标类$y$的关系,如Word2vec里面,使用上下文预测下个单词的概率。
完整的训练方法,如使用softmax或者Logistic回归需要对每个训练数据计算所有类$y\in L$的概率$F(x,y)$,当$|L|$非常大的时候,训练将非常耗时。
“candidate sampling"训练方法包括为每一个训练数据$(x_i,T_i)$构造一个训练任务,使得我们只需要使用一个较小的候选集合$C_i\in L$,就能评估$F(x,y)$,典型的,candidate set $C_i$包含目标类别$T_i$和一些随机采样的类别$S_i\in L$:$C_i = T_i \cup S_i$ , $S_i$的选择可能依赖 $x_i$和 $T_i$,也可能不依赖。 $F(x,y)$可以使用神经网络计算来表征(也就是TensorFlow里面常用的logits)
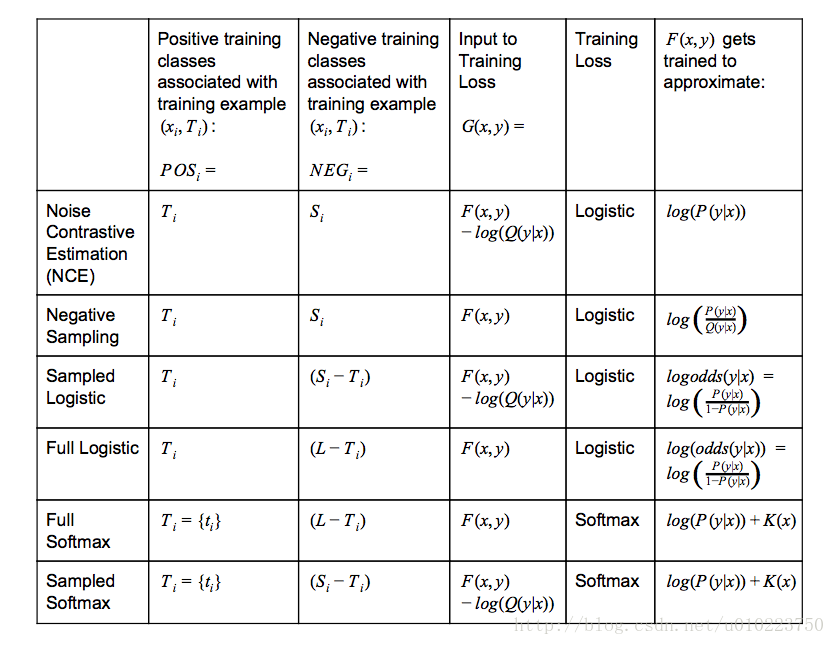
- $Q(y|x)$表示的是给定context $x_i$采样到$y$的概率
- $K(x)$表示任意不以来候选集的函数
- $logistic-training-loss = \sum_{i}(\sum_{y \in POS_i} log(1+exp(-G(x_i,y)) )+\sum_{y \in NEG_i} log(1+exp(G(x_i,y)) ))$
- $softmax-training-loss = \sum_{i}(-log(\frac{exp(G(x_i,t_i))}{\sum_{y \in POS_i \cup NEG_i} exp(G(x_i,y))}))$
在使用tensoflow的时候,我们有时候会纠结选择什么样的损失函数比较好,softmax和logistic在表达形式上是有点区别的,但是也不是很大,而且对于普通的softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits和sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits也都能够进行多分类任务,那么他们之间的区别是什么的?
就我个人所想到的,使用sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits和softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits的最大的区别是类别的排他性,在分类任务中,使用softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits我们一般是选择单个标签的分类,因为其具有排他性,说白了,softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits需要的是一个类别概率分布,其分布应该服从多项分布(也就是多项logistic regression),我们训练是让结果尽量靠近这种概率分布,不是说softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits不能进行多分,事实上softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits是支持多个类别的,其参数labels也没有限制只使用一个类别,当使用softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits进行多分类时候,以二类为例,我们可以设置真实类别的对应labels上的位置是0.5,0.5,训练使得这个文本尽量倾向这种分布,在test阶段,可以选择两个计算概率最大的类作为类别标签,从这种角度说,使用softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits进行多分,实际上类似于计算文本的主题分布。
对于sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits,公式可以看出,sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits其实是训练出了多个分类器,对于有n个标签的分类问题,其实质是分成了n个二分类问题,这点和softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits有着本质的区别。
tensorflow提供了下面两种candidate sample方法
- tf.nn.nce_loss
- tf.nn.sampled_softmax_loss
tf.nn.nce_loss使用的是logistic, 而tf.nn.sampled_softmax_loss采用的是softmax loss,其实这两者的区别也主要在这儿,采用logistic loss的本质上还是训练n个分类器,而使用softmax loss的其实只是训练了一个主题分类器,tf.nn.nce_loss主要思路也是判断给定context $C_i$和训练数据$x_i$,判断每一个$y_i$是不是target label,而 tf.nn.sampled_softmax_loss则是使得在target label上的分布概率最大化。
对于多标签多类别的分类任务使用Logistic比较好,对于多标签单类别的分类任务使用softmax比较好,采样中,采用tf.nn.sampled_softmax_loss训练cbow模型比较好,而 tf.nn.nce_loss训练skip-gram比较好。
tensorflow 源码解析:
_compute_sampled_logits输入隐藏层输出和真标签,在里面采样获得S集,并计算,返回的就是F(x,y)-logQ,在nce_loss和sampled_softmax_loss中都调用它进行采样,详细的源码解释在下面
|
|
_compute_sampled_logits的参数和返回
|
|